艾妈,终于跟进新版本流表匹配了。忧伤的故事是新版本内核匹配修改了好多,下放了部分wildcard matching到内核。源码看懂是没太大问题,逻辑还需要好好梳理一下。
1.datapatch内核流表匹配
datapath收到数据包的具体流程如下,艾妈,画得太丑,大家见谅:
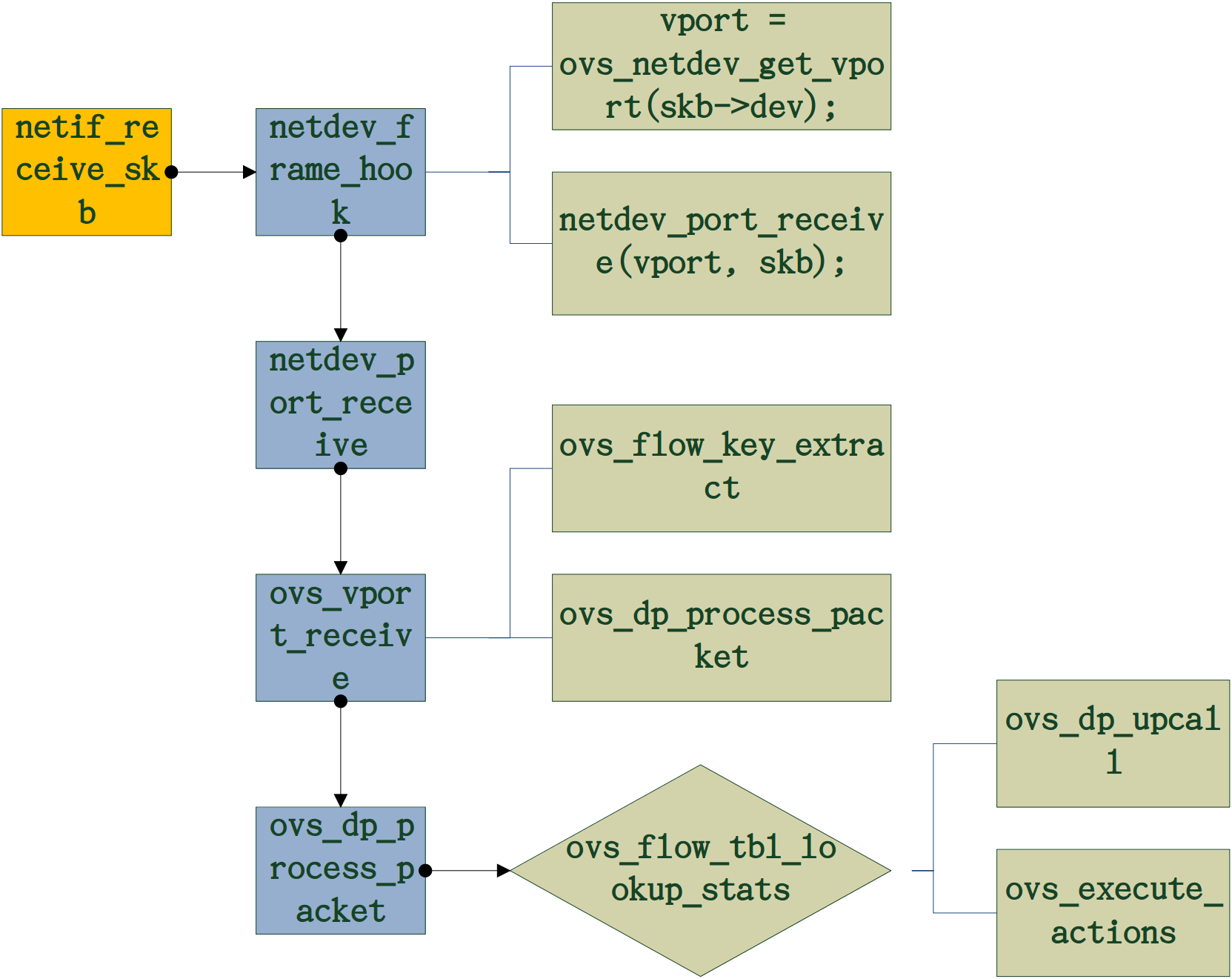 1.
1. neifreceive_skb是网卡收到包的函数,将会递送给netdev_frame_hook
2. netdev_frame_hook这个函数是vport初始化使注册的钩子函数,初始化vport流程(初始化vport => ovs_netdev_vport_ops => netdev_rx_handler_register)。它主要调用了两个函数:
(1) vport = ovs_netdev_get_vport(skb->dev); //获取对应dev的vport。(2)netdev_port_receive(vport, skb); //调用netdev_port_receive使指定vport进行收包。
3. netdev_port_receive首先检测skb是否被共享,若是则进行拷贝。 然后调用ovs_vport_receive。
4. ovs_vport_receive。
(1) 调用ovs_flow_key_extract基于SKB生成key值,并检查是否有错。
(2) 调用ovs_dp_process_packet。交付给datapath处理。
5. ovs_dp_process_packet。处理包,先查找包在内核流表中是否存在匹配的流表。再进行处理。
(1) ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats。基于前面生成的key值进行流表查找,返回匹配的流表项,结构为sw_flow。
(2) 若不存在匹配,则调用ovs_dp_upcall上传至user space进行匹配。 (包括包和key都要上传)
(3) 若存在匹配,则直接调用ovs_execute_actions执行对应的action,比如添加vlan头,转发到某个port等。
好吧,写到这,重头戏来了。到底内核流表匹配函数ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats都做了什么,是怎么发生匹配的?
首先,我来解释一下基本的名词:
- wildcard:wildcard表示匹配元组的掩码,openflow协议1.0中共有12项元组,包括:
inport,dl_src,dl_dst,dl_vlan,dl_vlan_pcp,dl_type,nw_tos,nw_proto,nw_src,nw_dst,tp_src,tp_dst这12个,掩码表示过滤部分元组。可以用一个12位的类型表示,一位代表一个元组,具体每项含义查看openflow协议。举个例子,比如掩码3这个数字在12位二进制中是0000000000011,那么可以表示tp_src,tp_dst给定,其余都不给定(这个顺序不一定刚刚是这两个元组) - 模糊匹配的意思是可以有1个或1个以上的元组不指定,而精确匹配则每个元组都必须指定。新版本中已经取消了facet和subfacet的概念。
来吧,上大图:
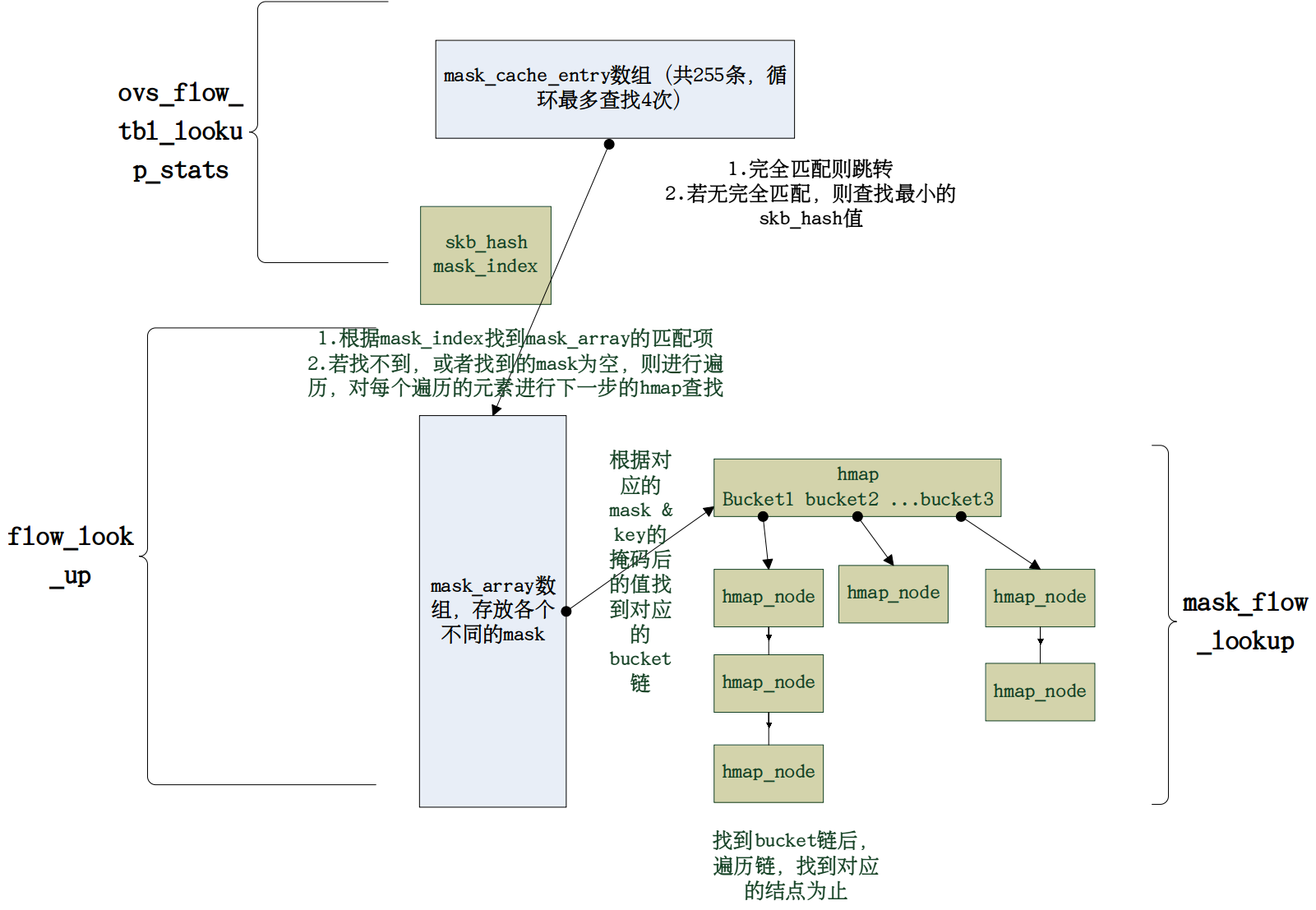
在2.0版本之前设计中,内核态只具有精确匹配,也就是每条匹配对应12元组信息,模糊匹配被放到用户态处理。2.0开始的版本将部分模糊匹配下放到内核态处理,以减少每次因为不同的包被递送时都要upcall到用户态处理的时间。
从逻辑上可以这么理解,内核具有两级流表:第1级为精确匹配所用的流表,第2级为模糊匹配所用的流表,第2级流表为带mask的匹配项,这个匹配项是之前包在内核态匹配没命中时upcall到用户态后,进行重新匹配所匹配中的那一项。比如一个包在递送到内核态,首先查找1级流表(后面我会详细说明其实查找顺序没有严格区分1,2级流表),没有命中则再次查找2级模糊匹配的流表项,如果还没命中则upcall到用户态,然后命中(没命中则会packet-in到controller),这时用户态的处理是将12元组的全部信息下放到内核态的1级流表,用于下次精确匹配;模糊匹配中的信息下放到内核态的2级流表,用于下次模糊匹配。
只不过作者在设计的时候没有严格区分内核态的1,2级流表,将两个流表合并为1个megaflow表,megaflow表中有mask_cache_entry, mask_array, hmap,查找也是将带mask的和不带mask的一块处理进行hash处理,首先查找mask_cache_entry表,命中的话则会根据查找到的mask_array的index去找到对应的mask,不命中的话则会遍历mask_array, 然后根据对应的mask和key值的掩码找到对应的hmap 中的bucket链,然后遍历这个bucket链。
啥?你问我为啥子在mask_cache_entry这么设计哈希,还带4次循环查找,每次查找8位。艾妈,这里我也不懂>_<。这个hash值是skb_get_hash后的结果,这个哈希函数是利用包的src, dst和port进行jhash处理后的结果。直觉告诉我这里很神奇,如果有谁知道,请一定告诉我~~
来吧,还是上个源码吧,不想看可以直接pass
首先是ovs_dp_process_packet:
/* Must be called with rcu_read_lock. */
void ovs_dp_process_packet(struct sk_buff *skb, struct sw_flow_key *key)
{
const struct vport *p = OVS_CB(skb)->input_vport;
struct datapath *dp = p->dp;
struct sw_flow *flow;
struct sw_flow_actions *sf_acts;
struct dp_stats_percpu *stats;
u64 *stats_counter;
u32 n_mask_hit;
stats = this_cpu_ptr(dp->stats_percpu);
/* Look up flow. */
flow = ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats(&dp->table, key, skb_get_hash(skb),
&n_mask_hit);
if (unlikely(!flow)) {
struct dp_upcall_info upcall;
int error;
upcall.cmd = OVS_PACKET_CMD_MISS;
upcall.userdata = NULL;
upcall.portid = ovs_vport_find_upcall_portid(p, skb);
upcall.egress_tun_info = NULL;
error = ovs_dp_upcall(dp, skb, key, &upcall);
if (unlikely(error))
kfree_skb(skb);
else
consume_skb(skb);
stats_counter = &stats->n_missed;
goto out;
}
ovs_flow_stats_update(flow, key->tp.flags, skb);
sf_acts = rcu_dereference(flow->sf_acts);
ovs_execute_actions(dp, skb, sf_acts, key);
stats_counter = &stats->n_hit;
out:
/* Update datapath statistics. */
u64_stats_update_begin(&stats->syncp);
(*stats_counter)++;
stats->n_mask_hit += n_mask_hit;
u64_stats_update_end(&stats->syncp);
}
我们关注ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats,用于查找流表,包括精确匹配和非精确匹配:
* mask_cache maps flow to probable mask. This cache is not tightly
* coupled cache, It means updates to mask list can result in inconsistent
* cache entry in mask cache.
* This is per cpu cache and is divided in MC_HASH_SEGS segments.
* In case of a hash collision the entry is hashed in next segment.
*/
struct sw_flow *ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats(struct flow_table *tbl,
const struct sw_flow_key *key,
u32 skb_hash,
u32 *n_mask_hit)
{
struct mask_array *ma = rcu_dereference(tbl->mask_array);
struct table_instance *ti = rcu_dereference(tbl->ti);
struct mask_cache_entry *entries, *ce;
struct sw_flow *flow;
u32 hash;
int seg;
*n_mask_hit = 0;
if (unlikely(!skb_hash)) {
u32 mask_index = 0;
return flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit, &mask_index);
}
/* Pre and post recirulation flows usually have the same skb_hash
* value. To avoid hash collisions, rehash the 'skb_hash' with
* 'recirc_id'. */
if (key->recirc_id)
skb_hash = jhash_1word(skb_hash, key->recirc_id);
ce = NULL;
hash = skb_hash;
entries = this_cpu_ptr(tbl->mask_cache);
/* Find the cache entry 'ce' to operate on. */
for (seg = 0; seg < MC_HASH_SEGS; seg++) { //循环查找4次 hash为32位,每次查找右移8位
int index = hash & (MC_HASH_ENTRIES - 1); //相与找到对应index
struct mask_cache_entry *e;
e = &entries[index]; //总共255项
if (e->skb_hash == skb_hash) { //如果命中 则进行跳转 根据找到的mask_index在mask_array中进行查找
flow = flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit,
&e->mask_index);
if (!flow)
e->skb_hash = 0;
return flow;
}
if (!ce || e->skb_hash < ce->skb_hash) //不命中则选择skb_hash值最小的
ce = e; /* A better replacement cache candidate. */
hash >>= MC_HASH_SHIFT; //右移8位
}
/* Cache miss, do full lookup. */
flow = flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit, &ce->mask_index); //未发生命中,根据之前选择的skb_hash值最小的进行mask_array中查找
if (flow)
ce->skb_hash = skb_hash;
return flow;
}
然后是flow_lookup,查找对应的流表项:
/* Flow lookup does full lookup on flow table. It starts with
* mask from index passed in *index.
*/
static struct sw_flow *flow_lookup(struct flow_table *tbl,
struct table_instance *ti,
const struct mask_array *ma,
const struct sw_flow_key *key,
u32 *n_mask_hit,
u32 *index)
{
struct sw_flow_mask *mask;
struct sw_flow *flow;
int i;
if (*index < ma->max) { //如果能直接找到对应的mask且不为空
mask = rcu_dereference_ovsl(ma->masks[*index]);
if (mask) {
flow = masked_flow_lookup(ti, key, mask, n_mask_hit);
if (flow)
return flow;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < ma->max; i++) { //找到的mask为空或者index超过max
if (i == *index)
continue;
mask = rcu_dereference_ovsl(ma->masks[i]);
if (!mask)
continue;
flow = masked_flow_lookup(ti, key, mask, n_mask_hit); //遍历进行下一级hmap查找,找到为止。由于每次循环都要进行下一级遍历,该语句复杂度较高
if (flow) { /* Found */
*index = i;
return flow;
}
}
return NULL;
}
然后是带mask的查找:
static struct sw_flow *masked_flow_lookup(struct table_instance *ti,
const struct sw_flow_key *unmasked,
const struct sw_flow_mask *mask,
u32 *n_mask_hit)
{
struct sw_flow *flow;
struct hlist_head *head;
int key_start = mask->range.start;
int key_end = mask->range.end;
u32 hash;
struct sw_flow_key masked_key;
ovs_flow_mask_key(&masked_key, unmasked, mask); //根据mask将unmasked映射到masked_key
hash = flow_hash(&masked_key, key_start, key_end); //过滤key中无关的字符,比如tunnel字段,并进行映射
head = find_bucket(ti, hash); //根据hash找到对应的hmap buckets
(*n_mask_hit)++;
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(flow, head, hash_node[ti->node_ver]) { //遍历查找
if (flow->mask == mask && flow->hash == hash &&
flow_cmp_masked_key(flow, &masked_key,
key_start, key_end)) //比较
return flow;
}
return NULL;
}
艾妈,下面就不贴了,接下来ovs_flow_mask_key根据mask将unmasked进行掩码,find_bucket就是找到对应的桶,flow_cmp_masked_key就是比较key值是否相同,用于判断是否是同一个flow。
2.vswitchd用户态流表匹配
这里我就不贴代码,我把我的理解说一下:
在老版本设计时用户态匹配是这么样搞的:n个hash table,每个hash table对应一个mask,比如hash table1对应的mask是ip src和ip dst,hash table2对应的是mac src和inport等等。而匹配时会遍历每一个hash table,如果命中则记录下该条记录的优先级,最后比较所有记录的优先级,选取最高优先级返回。如果最高优先级有多条,随机选择一条。
新一点的版本对其进行改进,因为遍历所有hash table的代价太高。做法就是将每个hash table中的优先级从高到低进行排序,假设发生命中,则不会再往下查找,因为继续查找到的优先级肯定低于当前优先级。如果不命中,则小于等于当前已经找到的优先级则停止,因为下面肯定不会有大于当前优先级的流表项。这样当遍历完所有的hash table后,优先级最高的一项也被选中。
而在最新的版本中,作者继续提出了一个优化概念:Staged Lookup。举个例子,比如某个hash table的mask是:“ingress port, L2 src, L3 src, L4 src”这么4个。则作者优化的方法是将之前的1个hash table扩展成为4个:分别是 (a)ingress port (b)ingress port, L2 src, (c)ingress port, L2 src, L3 src (d)ingress port, L2 src, L3 src, L4 src。就是说每个stage都是之前的多1个。这样当查找(a)表时,发生不命中,则没有必要再查找下面的(b)(c)(d)了,因为后面表都是前面表的前提上加1项,也不会发生命中。如果命中则跳转到下一级表,直至跳到最后为止。这样减少了一次性查找全部项的时间匹配代价。
说明
转载请著名出处:http://vinllen.com/ovs-2-3-datapatchnei-he-liu-biao-pi-pei-guo-cheng/
