hamp是ovs提供的一种哈希表的结构。
0. 普通hash表
以前我们用的哈希表结构一般是如下情况:
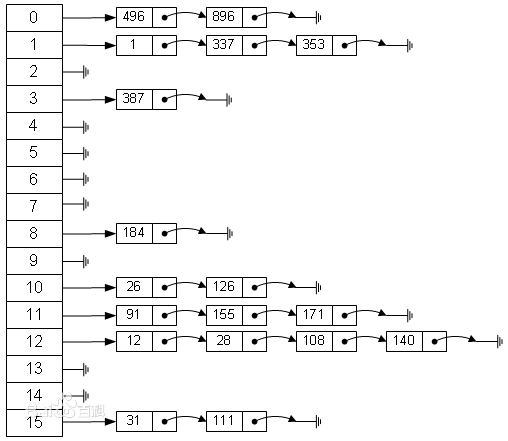
左边为一维数组,每个数组元素对应一个映射之后的hash值,每个数组元素对应一条单向链表,该单向链表中所有元素的值域在哈希映射之后一致,且都为表头数组元素的值。链表中一般包含两个域,一个为值域,另一个为指针域。好的哈希映射函数应该使每条链上的长度差不多,而不是某条过长。装填因子的概念就是:散列表中的元素个数与散列表大小的比值。
1. hmap结构
而hmap的结构与之非常相似,其结构如下:
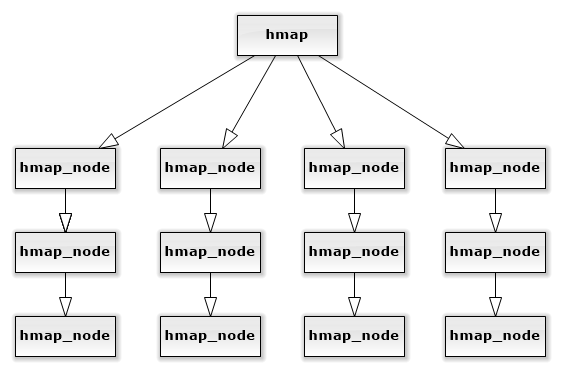
hmap为hash表总节点,其结构如下:
/* A hash map. */
struct hmap {
struct hmap_node **buckets; /* Must point to 'one' iff 'mask' == 0. */
struct hmap_node *one;
size_t mask;
size_t n;
};
- buckets为指向hmap_node结构的二维指针,相当于之前所说的hash表中的一维数组,当mask为0时指向one节点。
- one为特殊节点,如上所说。
- mask为掩码,同一条单向链表的所有元素的值在经过与掩码“与运算”之后的值一致。
- n表示hmap_node的节点个数。
hmap_node为表中的节点,其结构包括一个值域(hash值)和一个指针域(后向指针):
/* A hash map node, to be embedded inside the data structure being mapped. */
struct hmap_node {
size_t hash; /* Hash value. */
struct hmap_node *next; /* Next in linked list. */
};
2. hmap操作
本节介绍关于hamp的操作,包括初始化,删除,插入等。
2.1 初始化
/* Initializes 'hmap' as an empty hash table. */
void
hmap_init(struct hmap *hmap)
{
hmap->buckets = &hmap->one;
hmap->one = NULL;
hmap->mask = 0;
hmap->n = 0;
}
这个比较简单,需要说明的是初始掩码为0。
2.2 删除
整体删除,当表内buckets指针指向one时,直接free:
/* Frees memory reserved by 'hmap'. It is the client's responsibility to free
* the nodes themselves, if necessary. */
void
hmap_destroy(struct hmap *hmap)
{
if (hmap && hmap->buckets != &hmap->one) {
free(hmap->buckets);
}
}
hmap_clear为清除节点数据,但不释放内存:
/* Removes all node from 'hmap', leaving it ready to accept more nodes. Does
* not free memory allocated for 'hmap'.
*
* This function is appropriate when 'hmap' will soon have about as many
* elements as it before. If 'hmap' will likely have fewer elements than
* before, use hmap_destroy() followed by hmap_clear() to save memory and
* iteration time. */
void
hmap_clear(struct hmap *hmap)
{
if (hmap->n > 0) {
hmap->n = 0;
memset(hmap->buckets, 0, (hmap->mask + 1) * sizeof *hmap->buckets);
}
}
删除单个节点:
/* Removes 'node' from 'hmap'. Does not shrink the hash table; call
* hmap_shrink() directly if desired. */
static inline void
hmap_remove(struct hmap *hmap, struct hmap_node *node)
{
struct hmap_node **bucket = &hmap->buckets[node->hash & hmap->mask];//选择一维数组的头,也就是寻找相同mask之后值的单链表表头
while (*bucket != node) {
bucket = &(*bucket)->next;
}
*bucket = node->next;//注意bucket是二维指针,此操作相当于删除节点,并把指针域指向下一个节点
hmap->n--;
}
2.3 插入
在hmap中插入节点:
/* Inserts 'node', with the given 'hash', into 'hmap'. 'hmap' is never
* expanded automatically. */
static inline void
hmap_insert_fast(struct hmap *hmap, struct hmap_node *node, size_t hash)
{
struct hmap_node **bucket = &hmap->buckets[hash & hmap->mask]; //参见hmap_remove
node->hash = hash;
node->next = *bucket; //头插法
*bucket = node;
hmap->n++;
}
hmap_insert_at插入操作,涉及bucket的扩张:
/* Inserts 'node', with the given 'hash', into 'hmap', and expands 'hmap' if
* necessary to optimize search performance.
*
* ('where' is used in debug logging. Commonly one would use hmap_insert() to
* automatically provide the caller's source file and line number for
* 'where'.) */
static inline void
hmap_insert_at(struct hmap *hmap, struct hmap_node *node, size_t hash,
const char *where)
{
hmap_insert_fast(hmap, node, hash); //包裹函数,调用hmap_insert_fast
if (hmap->n / 2 > hmap->mask) { //超过装填因子,需扩张
hmap_expand_at(hmap, where);
}
}
hmap_expand_at如下:
/* Expands 'hmap', if necessary, to optimize the performance of searches.
*
* ('where' is used in debug logging. Commonly one would use hmap_expand() to
* automatically provide the caller's source file and line number for
* 'where'.) */
void
hmap_expand_at(struct hmap *hmap, const char *where)
{
size_t new_mask = calc_mask(hmap->n); //根据n计算目前的最大容量
if (new_mask > hmap->mask) { //超过最大容量,进行扩张
COVERAGE_INC(hmap_expand);
resize(hmap, new_mask, where);
}
}
calc_mask计算最大容量,通过位运算方式:
static size_t
calc_mask(size_t capacity)
{
size_t mask = capacity / 2;
mask |= mask >> 1;
mask |= mask >> 2;
mask |= mask >> 4;
mask |= mask >> 8;
mask |= mask >> 16;
#if SIZE_MAX > UINT32_MAX
mask |= mask >> 32;
#endif
/* If we need to dynamically allocate buckets we might as well allocate at
* least 4 of them. */
mask |= (mask & 1) << 1;
return mask;
}
扩容后调整代码:
static void
resize(struct hmap *hmap, size_t new_mask, const char *where)
{
struct hmap tmp;
size_t i;
ovs_assert(is_pow2(new_mask + 1));
hmap_init(&tmp);
if (new_mask) {
tmp.buckets = xmalloc(sizeof *tmp.buckets * (new_mask + 1));
tmp.mask = new_mask;
for (i = 0; i <= tmp.mask; i++) {
tmp.buckets[i] = NULL;
}
}
for (i = 0; i <= hmap->mask; i++) {
struct hmap_node *node, *next;
int count = 0;
for (node = hmap->buckets[i]; node; node = next) {
next = node->next;
hmap_insert_fast(&tmp, node, node->hash);
count++;
}
if (count > 5) {
static struct vlog_rate_limit rl = VLOG_RATE_LIMIT_INIT(10, 10);
COVERAGE_INC(hmap_pathological);
VLOG_DBG_RL(&rl, "%s: %d nodes in bucket (%"PRIuSIZE" nodes, %"PRIuSIZE" buckets)",
where, count, hmap->n, hmap->mask + 1);
}
}
hmap_swap(hmap, &tmp);
hmap_destroy(&tmp);
}
扩容方法及性能总结如下:
插入后n ++,如果n / 2 > mask(超过规定的装填因子),则将进行扩容。扩容的方法如下:
1. 计算新的mask值,比如n为17,则mask的值为 n / 2 = 8后再按位或1(即各位都取1),mask = 15。简单来说,也就是将老的mask左移1位再低位取1。
2. 根据新的mask值构造新的hmap结构。对于新的mask为15,则将构造16个bucket,编号分别是0~15。
3. 将原来hmap结构中的node结点按新的 hash & mask 的值插入新的bucket。
4. 交换新旧两个hmap指针,达到更新的目的。
总结:
如果发生扩容,则代价较大,因为将重新分配一个hmap,并逐个遍历旧的hmap结点,并插入新的hmap中。同理收缩也是一样。
